In today’s fast-changing digital landscape, businesses are expected to deliver content across multiple platforms—websites, mobile apps, smart devices, digital kiosks, and even wearable technology. Traditional content management systems (CMS) like WordPress or Drupal have long been the backbone of website content delivery. However, with the increasing demand for flexibility, scalability, and omnichannel content delivery, a new solution has gained momentum: the Headless CMS.
This article explores the rise of headless CMS in web development, why it is becoming so popular, and how it is shaping the future of digital content management.
1. What is a Headless CMS?

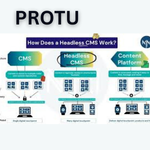
A headless CMS is a content management system that decouples the front end (“the head”) from the back end. Unlike traditional CMS platforms, where the content, design, and front-end delivery are tightly linked, a headless CMS focuses only on storing and managing content.
-
The back end manages content creation, editing, and storage.
-
The front end (website, app, or any digital interface) retrieves content via APIs (REST or GraphQL).
In simple terms: A headless CMS delivers content anywhere through APIs, giving developers full freedom to decide how and where it appears.
2. Traditional CMS vs. Headless CMS
| Feature | Traditional CMS (e.g., WordPress) | Headless CMS (e.g., Strapi, Contentful) |
|---|---|---|
| Content & Design | Tightly coupled | Fully separated |
| Delivery | Website-focused | Omnichannel (web, mobile, IoT, etc.) |
| Flexibility | Limited | High (front-end independent) |
| Performance | Can be slow with scaling | Faster, API-driven |
| Developer Freedom | Restricted to CMS templates | Free to use any framework or technology |
3. Why Headless CMS is Rising in Popularity
a) Omnichannel Content Delivery
With a headless CMS, businesses can deliver content across websites, mobile apps, smartwatches, AR/VR platforms, and IoT devices without duplicating efforts.
b) Developer Flexibility
Developers can use modern frameworks like React, Angular, Vue.js, or Next.js without being tied to CMS templates.
c) Scalability & Performance
API-first architecture ensures fast content delivery, even as businesses scale globally.
d) Future-Proof Technology
Since the back end is separate, businesses can easily adopt new front-end technologies without overhauling the entire system.
e) Improved Security
Because the front end and back end are decoupled, there is less exposure to direct attacks compared to traditional CMS platforms.
4. Key Use Cases of Headless CMS
-
E-commerce – Personalized shopping experiences across web, mobile, and in-store devices.
-
Media & Publishing – Delivering content to multiple digital channels simultaneously.
-
Corporate Websites – Faster updates and better performance for enterprise-scale websites.
-
Mobile Applications – Sharing a single content source across both web and mobile apps.
-
IoT & Smart Devices – Feeding content to smart TVs, voice assistants, and wearables.
5. Popular Headless CMS Platforms
Some of the most widely adopted headless CMS solutions include:
-
Contentful – Enterprise-grade, API-first CMS.
-
Strapi – Open-source, developer-friendly CMS with strong customization.
-
Sanity – Flexible content platform with real-time collaboration.
-
Prismic – Focused on speed and easy integration.
-
Ghost (when used in headless mode) – Popular among blogs and publishers.
6. Benefits for Businesses
-
Faster time to market – Content can be reused across multiple channels.
-
Enhanced customer experience – Consistent messaging on all platforms.
-
Cost efficiency – One content repository serves multiple digital products.
-
Future-ready – Businesses stay adaptable as new devices and platforms emerge.
7. Challenges of Headless CMS
While powerful, headless CMS adoption comes with challenges:
-
More developer involvement needed – Unlike WordPress, which is plug-and-play, headless CMS requires coding knowledge.
-
Learning curve – Teams must adapt to API-driven workflows.
-
Content previewing difficulties – Unlike traditional CMS, real-time preview of content changes may require extra setup.
-
Integration costs – Building custom front ends may add to initial development costs.
8. The Future of Headless CMS
With businesses moving toward digital-first strategies, headless CMS adoption is expected to grow rapidly. Trends that will shape the future include:
-
Composable architecture – Combining multiple headless services (CMS, e-commerce, analytics).
-
AI integration – Personalized content delivery powered by machine learning.
-
No-code/low-code tools – Easier adoption for non-technical users.
-
Hybrid CMS models – Offering both traditional and headless features for flexibility.
Conclusion
The rise of headless CMS reflects a shift in how businesses approach web development and digital experiences. Unlike traditional CMS platforms, headless solutions empower developers with freedom, improve scalability, and allow companies to deliver content seamlessly across multiple platforms.
As customer expectations grow for fast, personalized, and consistent experiences, headless CMS is becoming less of a trend and more of a necessity in modern web development.